What are Databases?
The concept of databases has existed for centuries in various forms. Before the digital era, data was stored physically on paper, in journals, and inside filing cabinets. While these methods served their purpose, they lacked efficiency, making information retrieval slow and cumbersome.
The advent of electronic databases revolutionized data storage, providing a structured and efficient way to manage information. This shift began in the 1960s, marking the birth of digital data storage.
Over time, different database models emerged, each improving upon the previous one:
Flat File Databases – The earliest form, where data was stored in simple text files with no structured relationships.
Hierarchical Databases – Organized in a tree-like structure, where parent-child relationships dictated data access.
Network Databases – Introduced more complex relationships, allowing data to have multiple connections rather than following a strict hierarchy.
These types of database structures were complicated to work with and in the 1980s the relational model of databases was introduced.
Relational Database
The Relational Database was introduced by E.F. Codd, marking a paradigm shift in the way data was stored and managed. His invention introduced a structured, systematic approach to organizing information, making data storage more efficient and accessible.
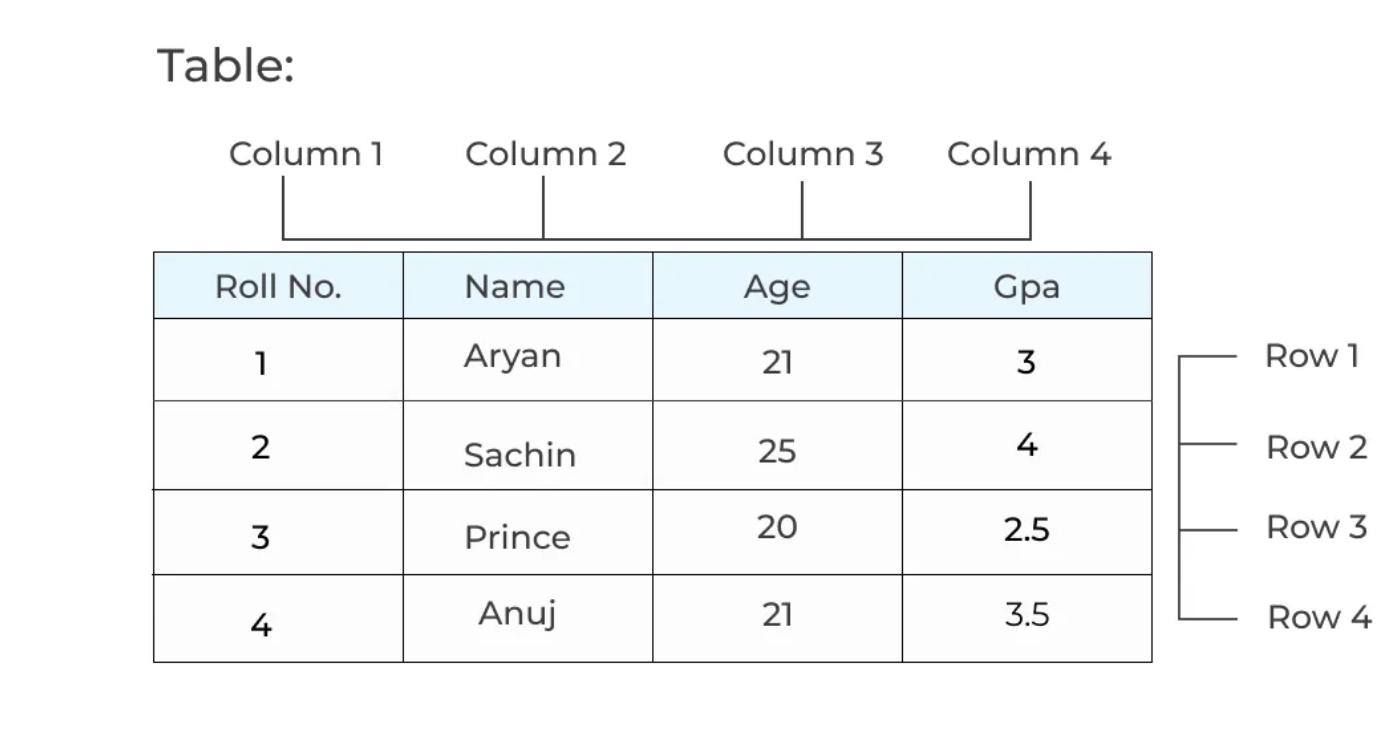
A relational database is built on the concept of tables, where data is arranged in rows and columns. Each row, also known as a record, holds the actual data, while each column represents the properties or attributes of that data. This model provided a more flexible and scalable way to store and retrieve information, laying the foundation for modern database systems.
In the 1990s, the Object-Oriented Database Model was introduced, aligning with the rise of Object-Oriented Software Design. This model allowed databases to store data as objects, mirroring the principles of object-oriented programming.
As the internet continued to grow, there was a rising need for databases that could handle high-speed data retrieval efficiently. This led to the introduction of NoSQL databases, designed to allow fast reads and scalability. NoSQL databases are widely used by major companies such as Facebook and Google, where rapid data access is crucial. Additionally, Amazon leverages this model for its DynamoDB, providing a scalable and high-performance database solution.
Database technology continues to evolve, and today, we see the rise of Cloud Databases, offering scalable, on-demand storage solutions that power modern applications.